Loading content...
- Software DevelopmentIT Consulting & DesignAI & Data SolutionsQuality AssuranceTeam & Resource SupportBusiness Support Services
Middleware is a crucial component of web development in .NET Core, managing how HTTP requests and responses flow through your application. Learn how to build custom middleware to enforce security, logging, and performance enhancements.
Custom middleware adds layers of validation and authorization.
Centralized logging through middleware enhances visibility.
Inline logic simplifies debugging and request tracing.
Loading content...
Let's discuss your project and create a custom web application that drives your business forward. Get started with a free consultation today.

Middleware is a crucial component of web development in .NET Core, managing how HTTP requests and responses are processed. It consists of software components in the ASP.NET Core request pipeline that handle various aspects of the request/response lifecycle, such as:
This modular approach enhances flexibility, maintainability, and reusability, making middleware a powerful tool in modern application design.
In this blog, we’ll explore how to use middleware in .NET, when and where it should be used, key considerations, and best case studies to help you implement it effectively.
Middleware functions as a series of components within the ASP.NET Core request pipeline. Requests traverse this pipeline, with each middleware component processing sequentially. It is executed in the order they are registered.
This flow ensures a controlled and organized approach to request and response handling.
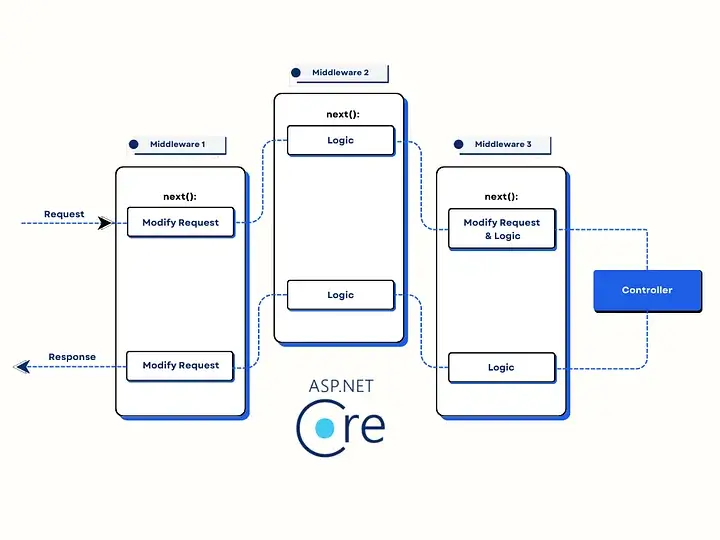
A request pipeline can consist of built-in middleware, third-party middleware, or custom middleware such as logging middleware and exception middleware.
Middleware in ASP.NET Core is categorized based on its functionality and purpose. Below are the key types:
Understanding middleware types helps in designing efficient and secure ASP.NET Core applications.
Middleware is configured in the Program.cs file, particularly within the Configure method. We can add middleware based on the type.
ASP.NET Core provides several predefined middleware components for common tasks.
You can find list of predefined middleware below:
Routing
Manages request routing in the application.
Authentication
Handles user authentication.
Authorization
Handles user access control.
Exception Handling
Captures and processes unhandled exceptions.
Static File
Serves static files (CSS, JS, images) from the wwwroot folder.
CORS
Enables or restricts cross-origin HTTP requests.
Response Caching
Improves performance by caching responses.
Logging
Captures and logs request and response details.
Compression
Compresses response data to reduce bandwidth usage.
Here’s a basic example:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
public class Startup
{
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
// Logging Middleware
app.Use(async (context, next) =>
{
Console.WriteLine("Handling request: " + context.Request.Path);
await next.Invoke();
Console.WriteLine("Finished handling request.");
});
// Static Files Middleware
app.UseStaticFiles();
// Routing Middleware
app.UseRouting();
// Authentication Middleware
app.UseAuthentication();
// Endpoints Middleware
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllers();
});
}
}Developers can create their own middleware to handle specific application requirements.
Sometimes, built-in middleware won’t meet all your needs, and you’ll need to create custom middleware.
Here’s how to write simple middleware to log requests:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public class CustomLoggingMiddleware {
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
public CustomLoggingMiddleware(RequestDelegate next) {
_next = next;
}
public async Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext context) {
Console.WriteLine($"Request: {context.Request.Method} {context.Request.Path}");
await _next(context);
Console.WriteLine($"Response: {context.Response.StatusCode}");
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
// Extension method for easy addition to pipeline
public static class CustomLoggingMiddlewareExtensions {
public static IApplicationBuilder UseCustomLogging(this IApplicationBuilder builder)
{
return builder.UseMiddleware<CustomLoggingMiddleware>();
}
}1
2
// Use in Program.cs
app.UseCustomLogging();If you prefer not to register (Step 2), you can directly add the following in the Program.cs file:
1
app.UseMiddleware<CustomLoggingMiddleware>();Many third-party libraries offer additional middleware for logging, security, and monitoring. For example:
1
2
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI();1
app.UseHangfireDashboard();Middleware is essential for creating robust web applications, and here’s why:
Middleware is powerful but should be used carefully to avoid common pitfalls:
1
2
3
app.UseAuthentication(); // Must be before Authorization
app.UseAuthorization();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints => { endpoints.MapControllers(); });If UseAuthorization() comes before UseAuthentication(), authorization will fail.
await _next(context); in custom middleware to ensure the next middleware in the pipeline gets executed.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
try
{
await _next(context);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error: {ex.Message}");
}async methods wherever possible.Middleware finds its place in nearly every aspect of an ASP.NET Core web application:
Investigate how components can rely on services registered in the Dependency Injection (DI) container. Provide examples of injecting such as logging, configuration, or data access into middleware.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public class LoggingMiddleware
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
private readonly ILogger<LoggingMiddleware> _logger;
public LoggingMiddleware(RequestDelegate next, ILogger<LoggingMiddleware> logger)
{
_next = next;
_logger = logger;
}
public async Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext context)
{
_logger.LogInformation($"Request Path: {context.Request.Path}");
await _next(context);
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
var app = builder.Build();
app.UseMiddleware<LoggingMiddleware>(); // Registers middleware
app.Run();Developers can configure middleware to execute conditionally based on request properties, such as HTTP methods, headers, or paths.
MapWhen to create conditional middleware:1
2
3
4
app.MapWhen(context => context.Request.Path.StartsWithSegments("/api"), appBuilder =>
{
appBuilder.UseMiddleware<ApiSpecificMiddleware>();
});Middleware components are executed in a pipeline. If a middleware does not call await _next(context), it short-circuits the pipeline, preventing the request from reaching the next middleware or endpoint.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
public class AuthorizationMiddleware
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
public AuthorizationMiddleware(RequestDelegate next)
{
_next = next;
}
public async Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext context)
{
if (!context.User.Identity.IsAuthenticated)
{
context.Response.StatusCode = 401; // Unauthorized
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Access Denied");
return; // Short-circuits the pipeline
}
await _next(context);
}
}Sometimes middleware should be enabled or disabled dynamically based on settings. Use feature flags to enable or disable middleware dynamically. Helps in performance tuning and A/B testing.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
var enableLogging = true;
app.Use(async (context, next) =>
{
if (enableLogging)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Request: {context.Request.Method} {context.Request.Path}");
}
await next();
});Use feature flags to enable or disable middleware dynamically. Helps in performance tuning and A/B testing.
Middleware can modify responses, such as adding custom headers.
1
2
3
4
5
6
app.Use(async (context, next) =>
{
await next();
context.Response.Headers.Add("X-Frame-Options", "DENY");
context.Response.Headers.Add("X-Content-Type-Options", "nosniff");
});Modify headers to enhance security. Ensure response modifications are done after await next().
Debugging middleware in ASP.NET Core is essential for identifying and resolving issues in the request pipeline. Since middleware executes sequentially, any misconfiguration or failure can affect the entire application. Here’s how you can effectively debug and diagnose middleware issues:
1
2
3
4
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
} Microsoft.AspNetCore.Diagnostics.1
app.UseMiddleware<DiagnosticMiddleware>();Middleware in .NET Core is a fundamental concept that allows developers to build scalable, maintainable, and secure web applications. By understanding its purpose, use cases, and implementation, you can create flexible pipelines that handle requests and responses efficiently.
Start exploring middleware in your .NET Core projects to unlock its full potential!